고정 헤더 영역
상세 컨텐츠
본문
1. 필요한 모듈 불러오기
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torchvision import transforms, datasets2. GPU 사용가능 여부 확인
if torch.cuda.is_available() :
DEVICE = torch.device('cuda')
else :
DEVICE = torch.device('cpu')
print('Using PyTorch version :', torch.__version__, ' Device :', DEVICE)3. 데이터 불러오기
BATCH_SIZE = 32
EPOCHS = 10
train_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root = "../data/MNIST",
train = True,
download = True,
transform = transforms.ToTensor())
test_dataset = datasets.MNIST(root = "../data/MNIST",
train = False,
transform = transforms.ToTensor())
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset = train_dataset,
batch_size = BATCH_SIZE,
shuffle = True)
test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset = test_dataset,
batch_size = BATCH_SIZE,
shuffle = False)4. 데이터 확인 및 시각화
- 데이터 size 및 type 확인
for (X_train, y_train) in train_loader :
print('X_train :', X_train.size(), 'type :', X_train.type())
print('y_train :', y_train.size(), 'type :', y_train.type())
break
#X_train : torch.Size([32, 1, 28, 28]) type : torch.FloatTensor
#y_train : torch.Size([32]) type : torch.LongTensor- 이미지 확인
plt.figure(figsize = (10, 1))
for i in range(10):
plt.subplot(1, 10, i + 1)
plt.axis('off')
plt.imshow(X_train[i, :, :, :].numpy().reshape(28, 28), cmap = "gray_r")
plt.title('Class: ' + str(y_train[i].item()))
5. 모델링
- MLP 모델 설계
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(28 * 28, 512)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(512, 256)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(256, 10)
self.dropout_prob = 0.5
self.batch_norm1 = nn.BatchNorm1d(512)
self.batch_norm2 = nn.BatchNorm1d(256)
def forward(self, x):
x = x.view(-1, 28 * 28)
x = self.fc1(x)
x = self.batch_norm1(x)
x = F.relu(x)
x = F.dropout(x, training = self.training, p = self.dropout_prob)
x = self.fc2(x)
x = self.batch_norm2(x)
x = F.relu(x)
x = F.dropout(x, training = self.training, p = self.dropout_prob)
x = self.fc3(x)
return x- Optimizer, He-initialization 적용
import torch.nn.init as init
def weight_init(m):
if isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
init.kaiming_uniform_(m.weight.data)
model = Net().to(DEVICE)
model.apply(weight_init)
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr = 0.01)
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
print(model)6. 모델 학습
- train 데이터에 대한 모델 성능을 확인하는 함수 정의
def train(model, train_loader, optimizer, log_interval):
model.train()
for batch_idx, (image, label) in enumerate(train_loader):
image = image.to(DEVICE)
label = label.to(DEVICE)
optimizer.zero_grad()
output = model(image)
loss = criterion(output, label)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if batch_idx % log_interval == 0:
print("Train Epoch: {} [{}/{} ({:.0f}%)\tTrain Loss: {:.6f}".format(
epoch, batch_idx * len(image), len(train_loader.dataset), 100 * batch_idx / len(train_loader),
loss.item()
))- test 데이터에 대한 모델 성능을 확인하는 함수 정의
def evaluate(model, test_loader):
model.eval()
test_loss = 0
correct = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for image, label in test_loader :
image = image.to(DEVICE)
label = label.to(DEVICE)
output = model(image)
test_loss += criterion(output, label).item()
prediction = output.max(1, keepdim = True)[1]
correct += prediction.eq(label.view_as(prediction)).sum().item()
test_loss/= len(test_loader.dataset)
test_accuracy = 100. * correct / len(test_loader.dataset)
return test_loss, test_accuracy- 모델 학습
loss = []
accuracy = []
for epoch in range(1, EPOCHS + 1):
train(model, train_loader, optimizer, log_interval = 200)
test_loss, test_accuracy = evaluate(model, test_loader)
loss.append(test_loss)
accuracy.append(test_accuracy)
print("|n[EPOCH:{}], \tTest Loss: {:.4f}, \tTest Accuracy: {:.2f} % \n".format(
epoch, test_loss, test_accuracy
))7. 결과 확인
plt.figure(figsize=(10,5))
plt.subplot(1,2,1)
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.plot(loss)
plt.subplot(1,2,2)
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.plot(accuracy)
plt.show()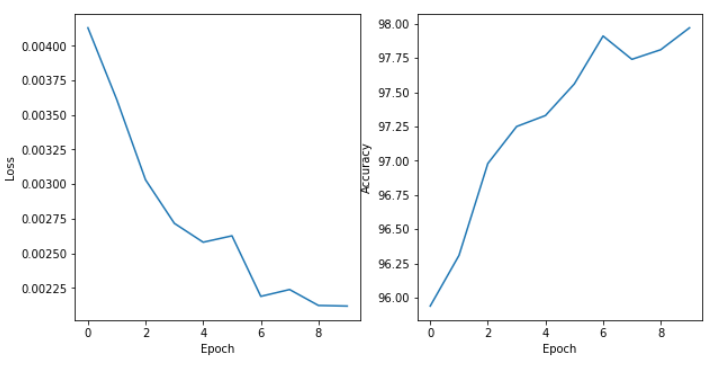
학습이 진행되면서 Loss값은 감소하고 약 98%의 정확도가 나왔다.





댓글 영역